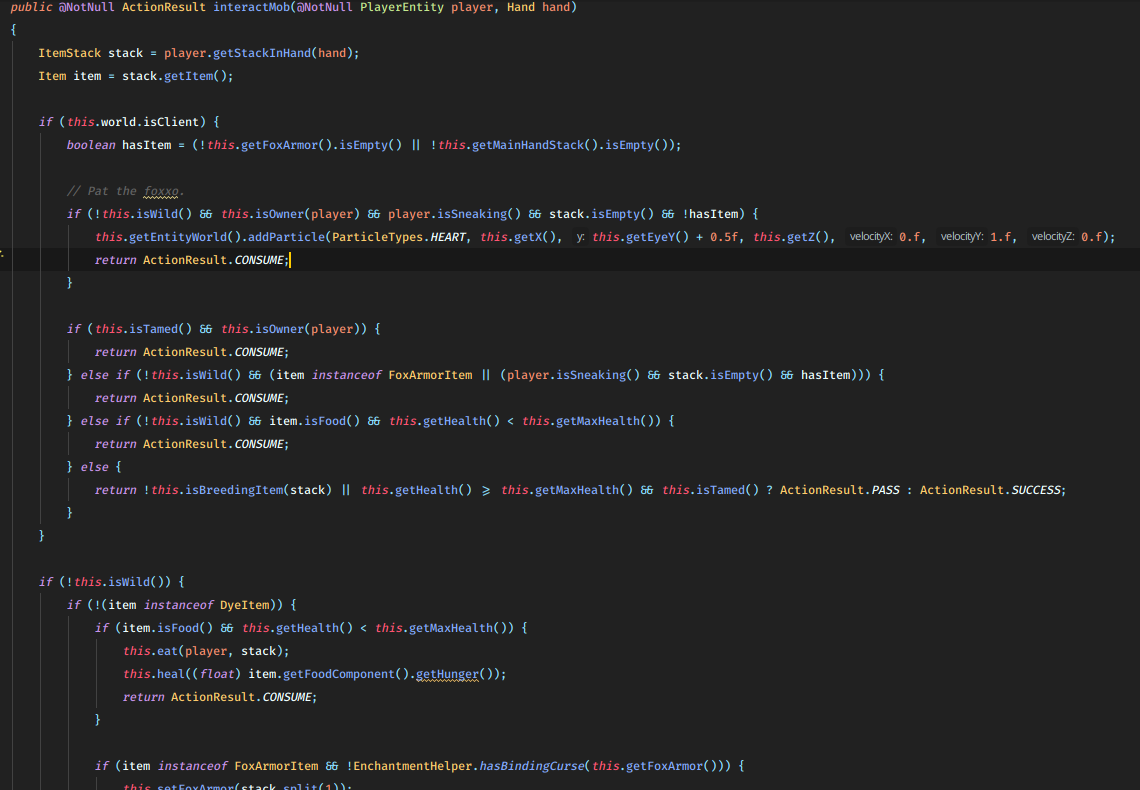
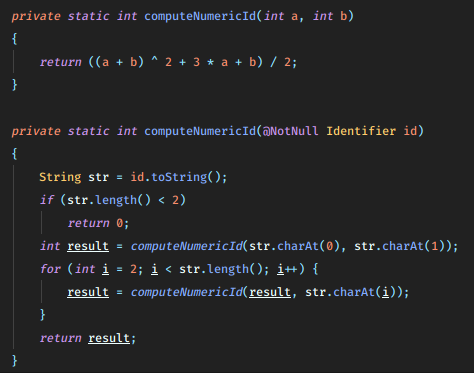
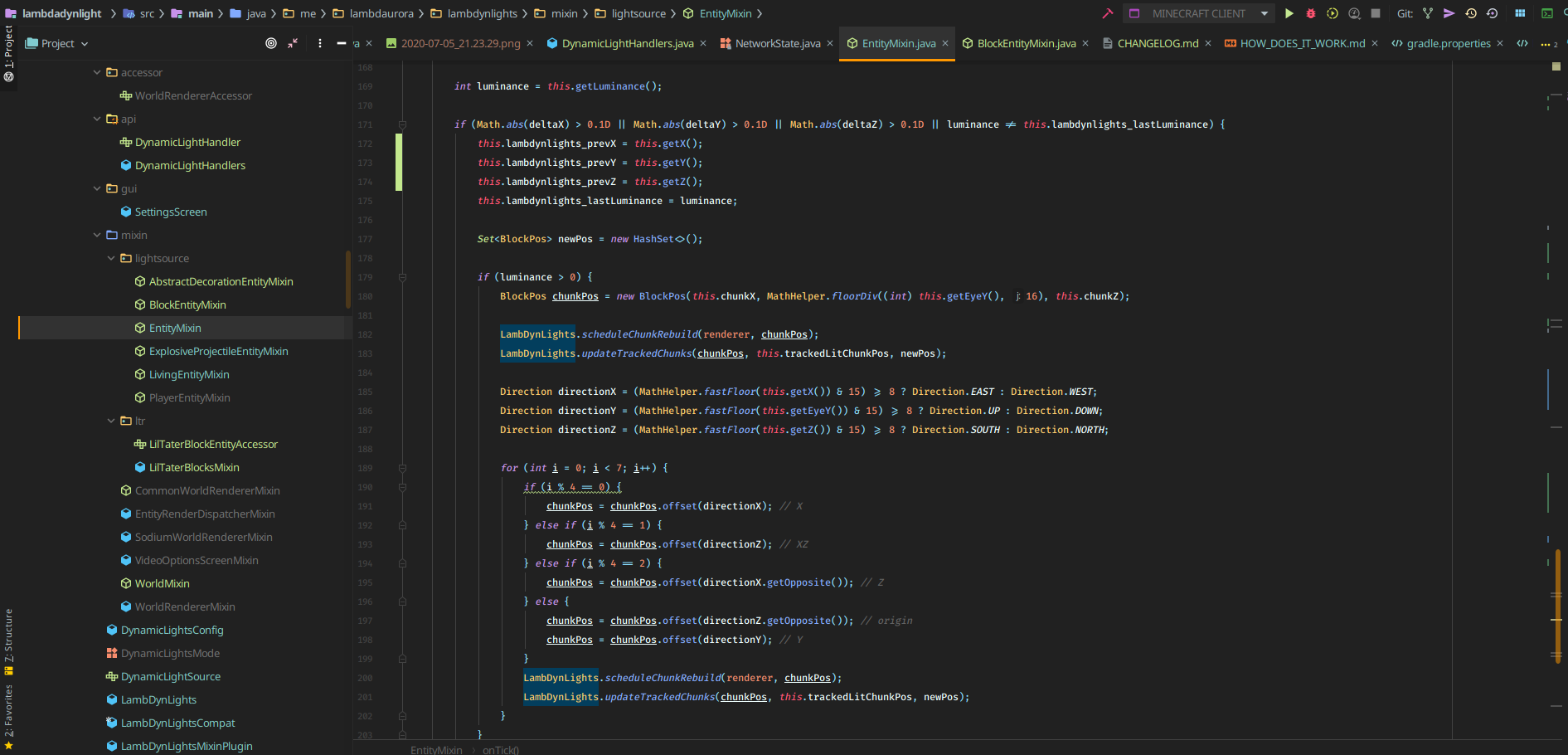
namespace:name which is great for modding, to break the less things possible I made that it still associates a numerical id. But how does it work? The goal was to use a ℕ^n -. But how with strings? I simply for-loop the string characters and use their ASCII/UTF-8 values to compute the numerical id!
Honestly I wasn't thinking that when modding I would involve Maths ahah. But it's good I think and it works :)
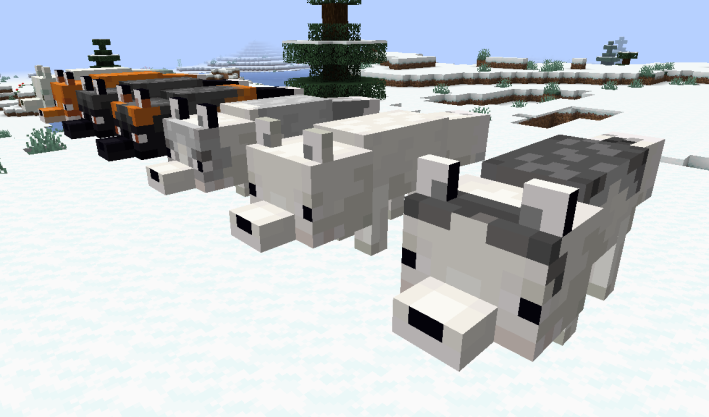
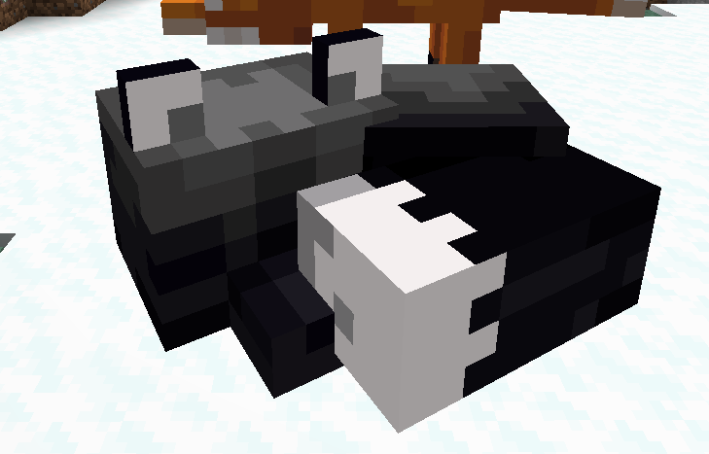
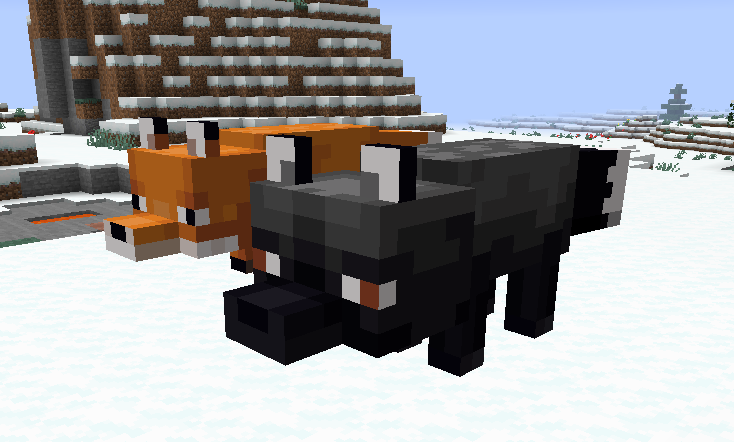
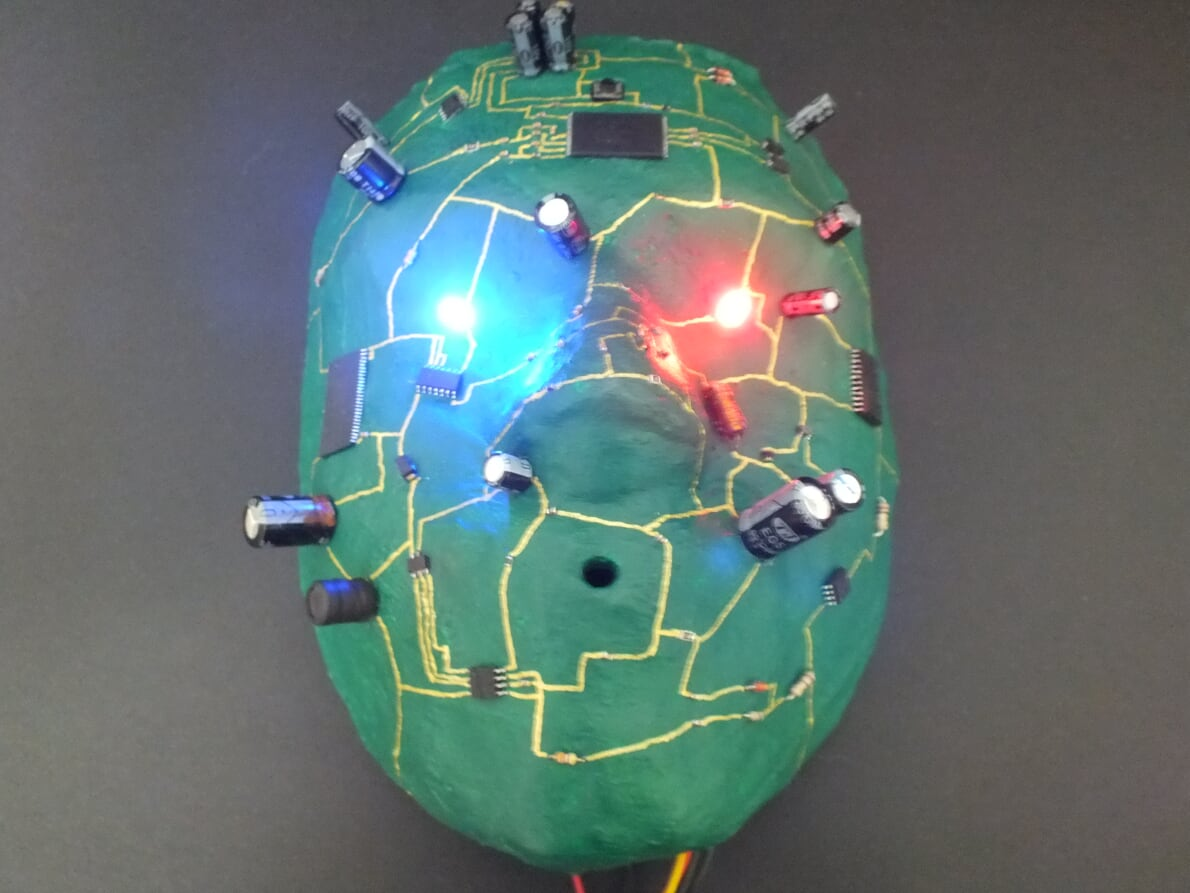
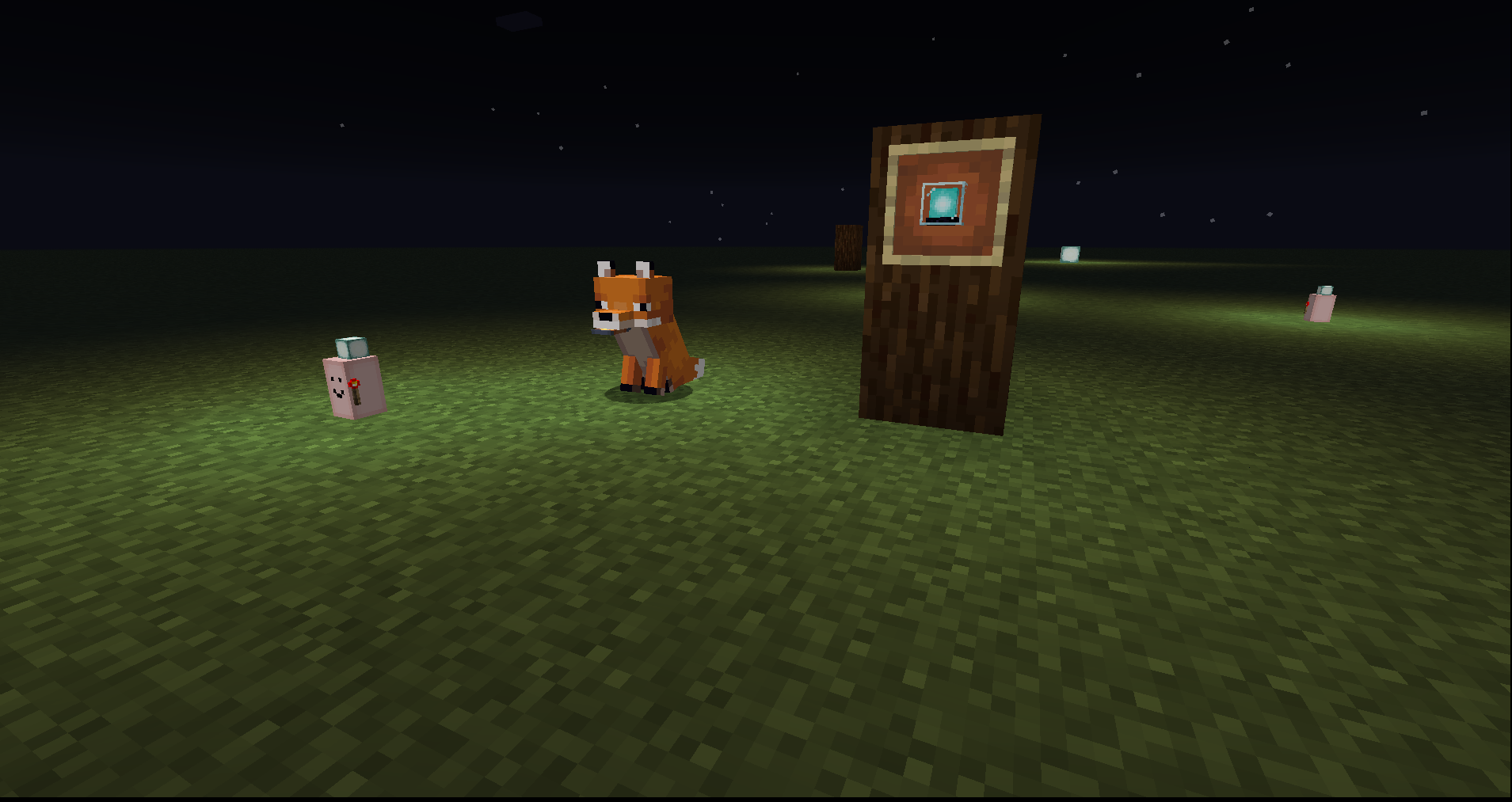
And I'm happy with the texture I made for the silver fox!
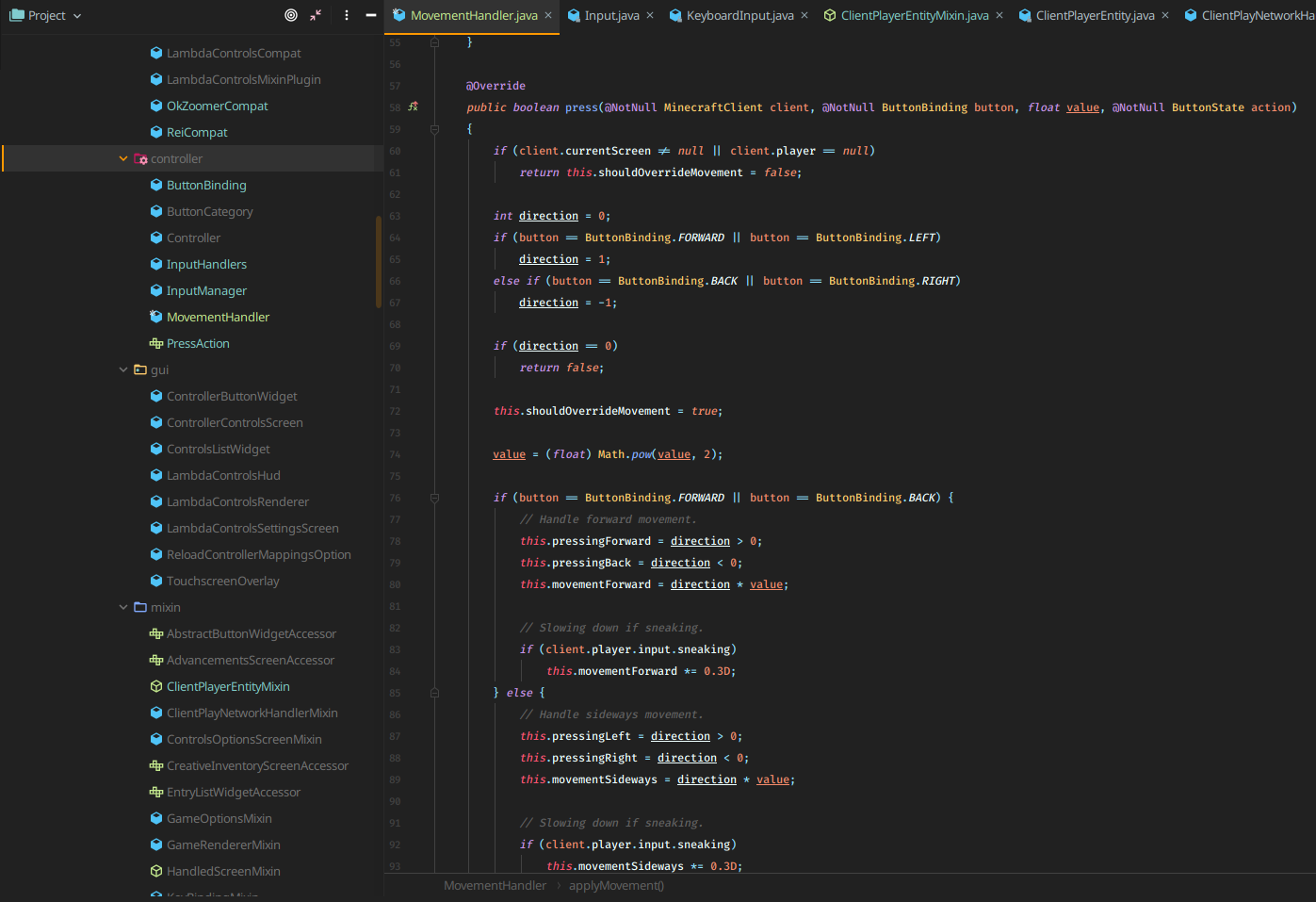
The other cool detail is it can technically work with Vanilla clients, they will not crash if they join a server with the mod, they will just see red foxes.ButtonBinding API (which manages bindings made with the controller buttons instead of KeyBinding which is for keyboard/mouse) to include the float value. It's really great to work on those kind of things as it will certainly help when making your own game! Everytime I implemented an input system I struggled but with this API I'll be able to make a more robust input system the day I'll make my own game!
The screenshot is an example implementation of a PressAction interface which handles the input actions of a ButtonBinding, and this one is also the analog movement implementation. :) public static int getRainbowRGB(double x, double y)
{
float speed = 2600.0F;
return Color.HSBtoRGB((float) ((System.currentTimeMillis() - x * 10.0D - y * 10.0D) % speed) / speed,
(float) AuroraKeystrokes.get().config.getRainbowSaturation(),
0.9F);
}
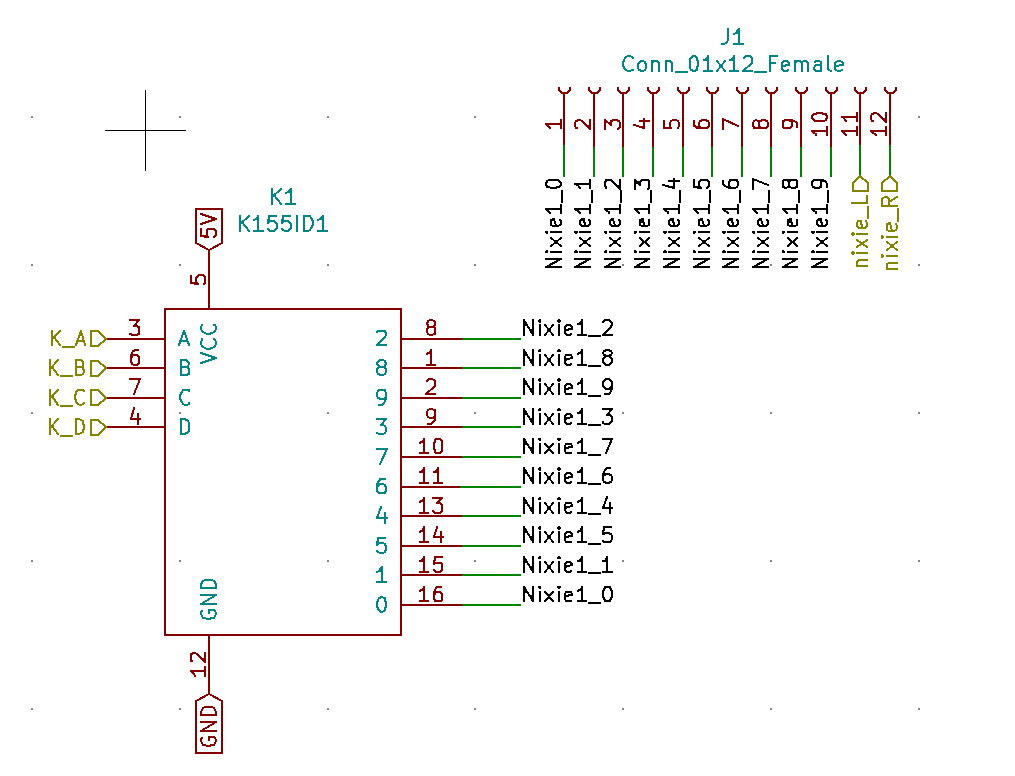
A bit difficult to find it at first but when found it gives a cool effect :)std::map orders alphabetically with string keys so I replaced it with a std::vector so I can keep the original order.
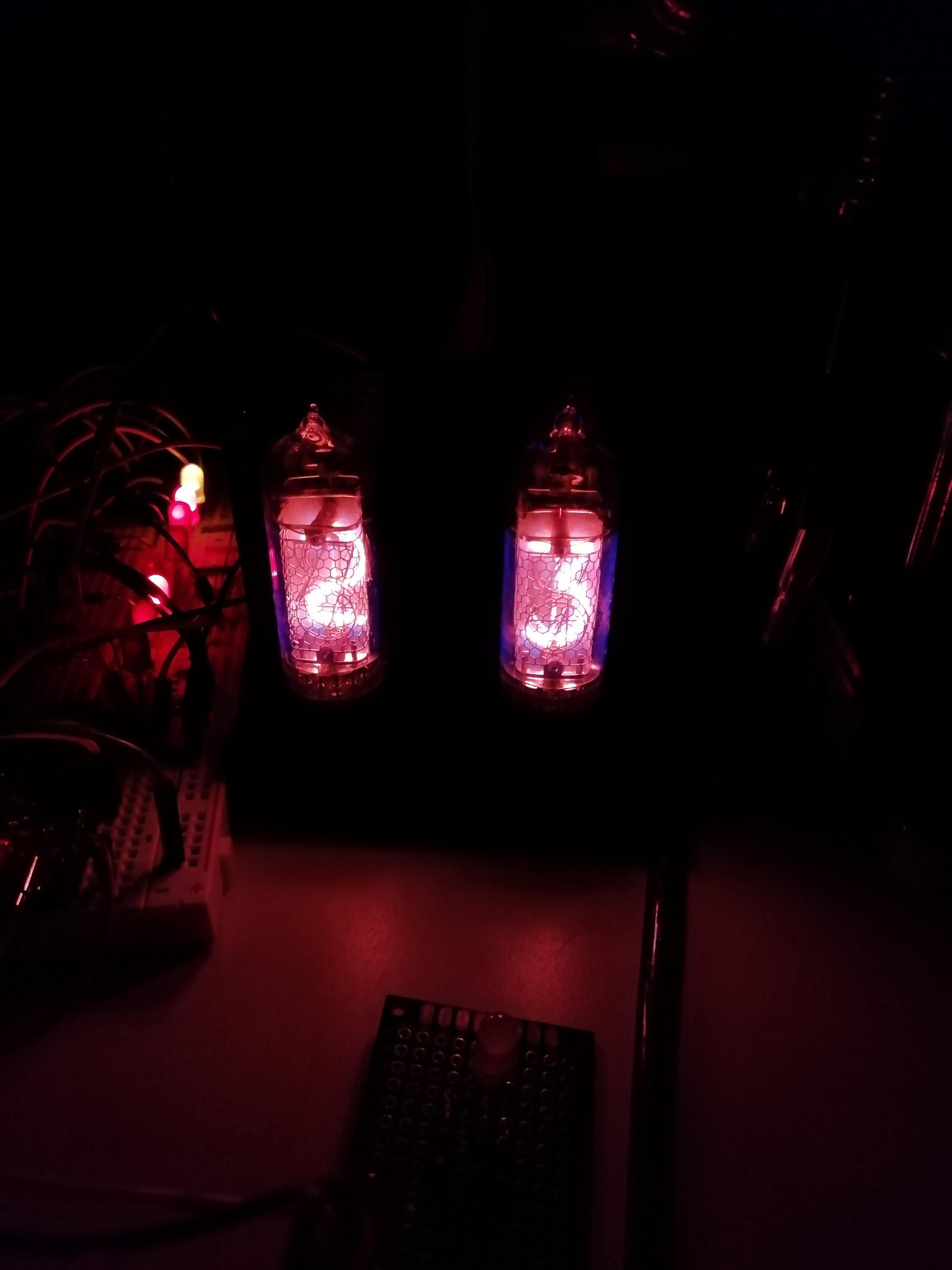
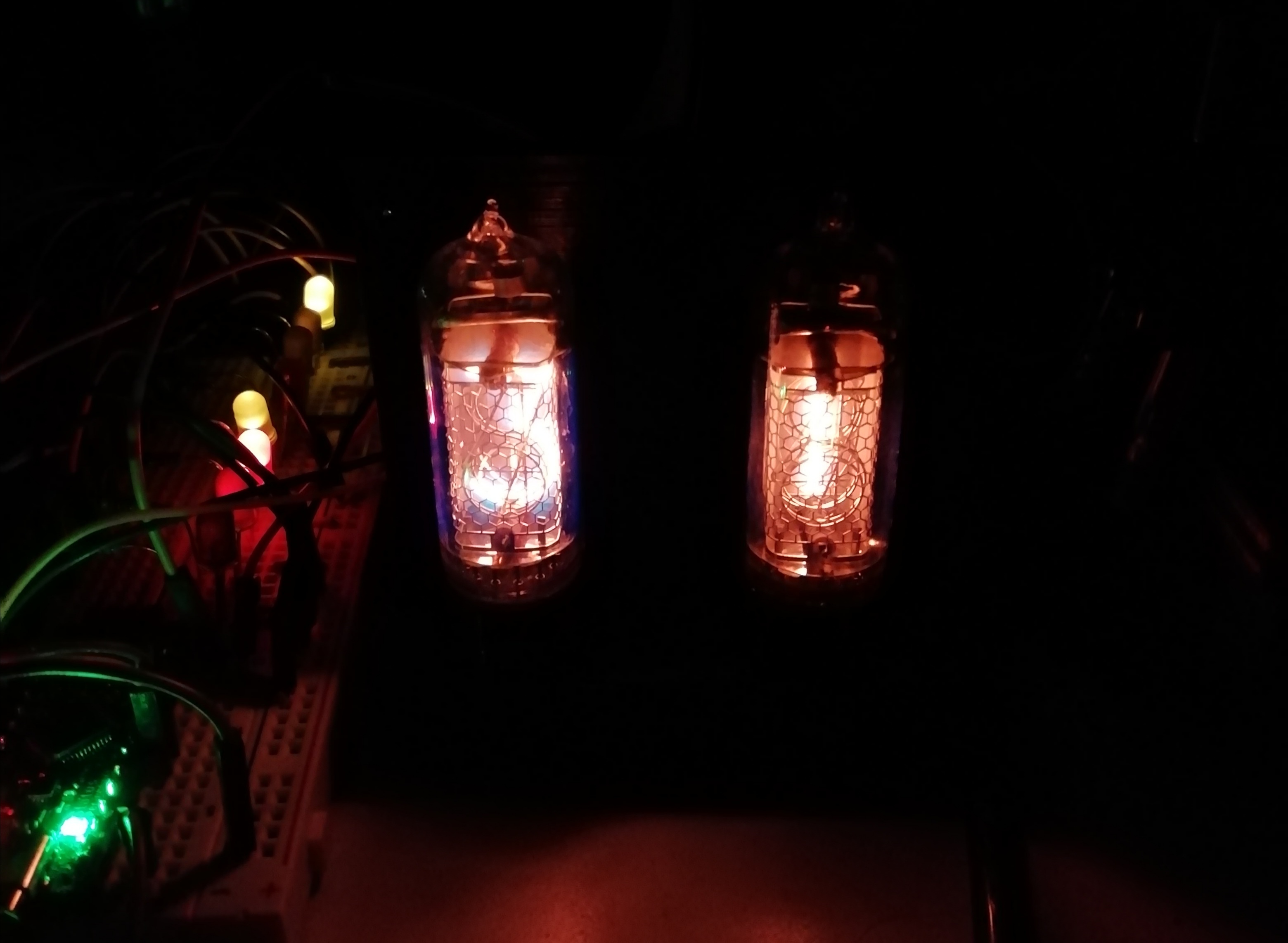
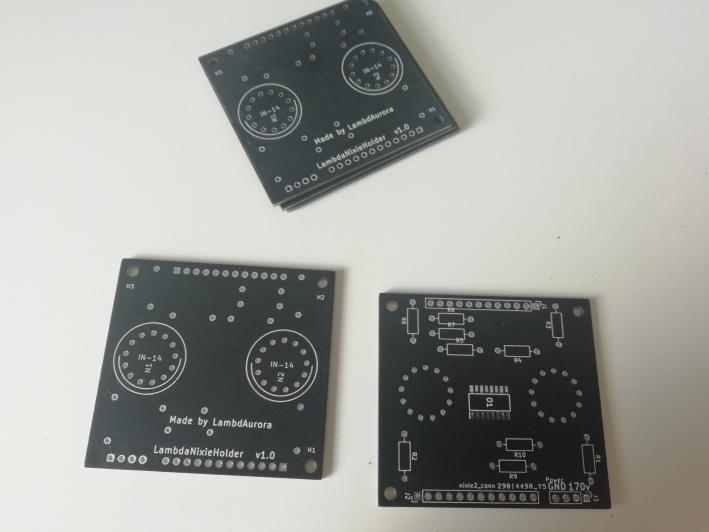
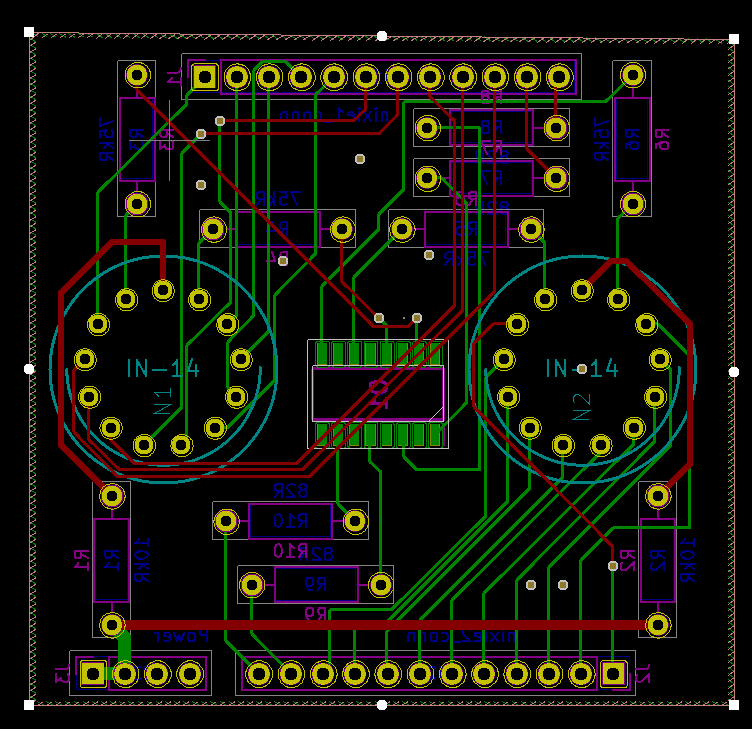
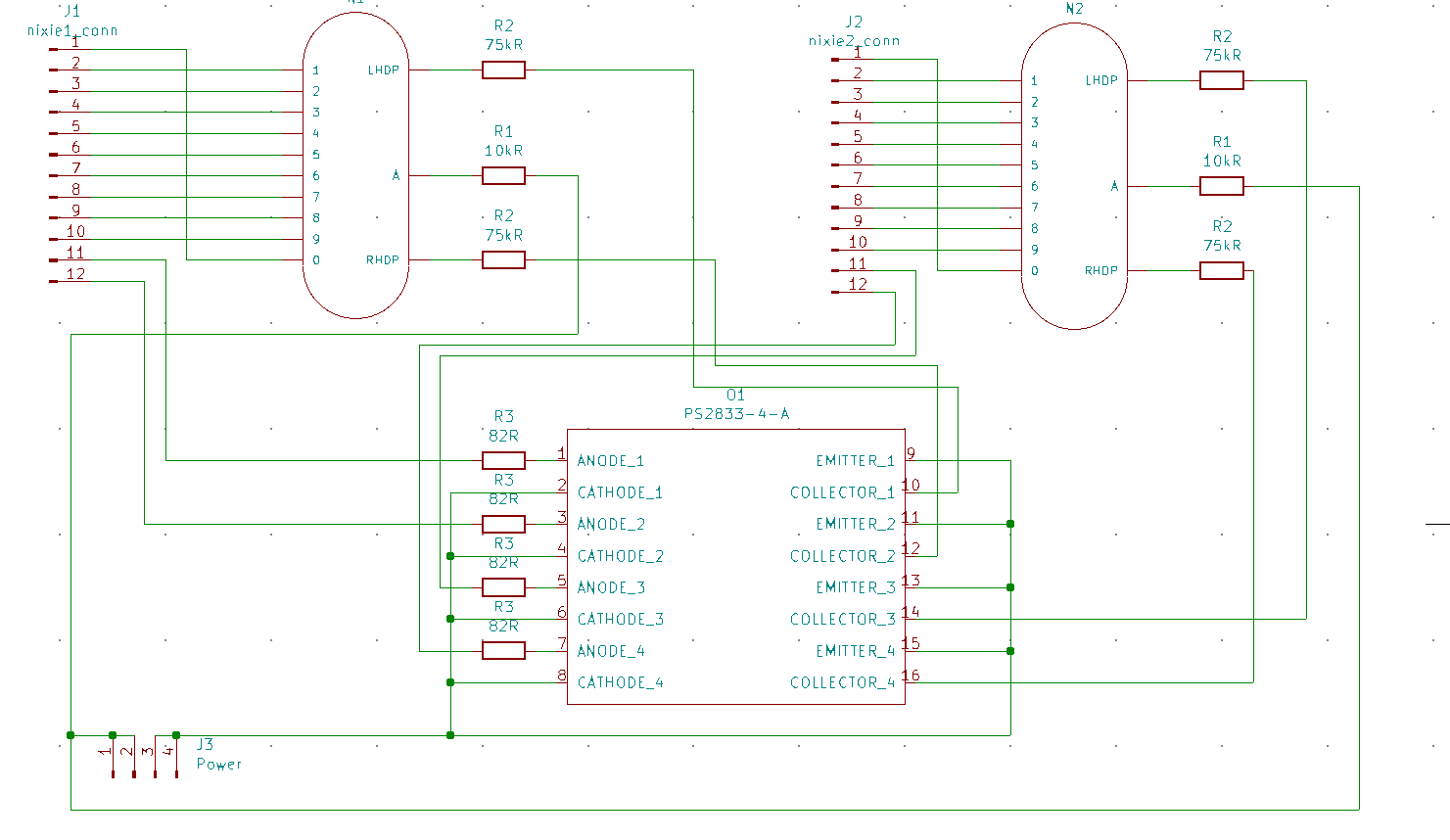
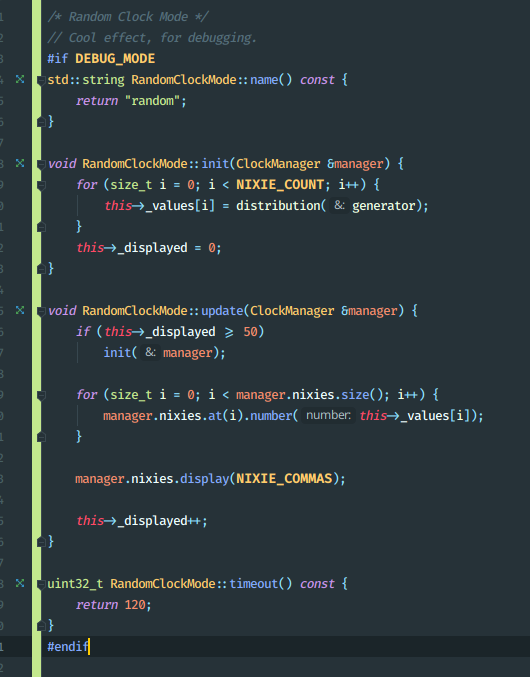
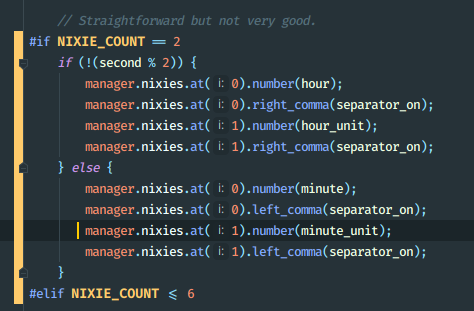
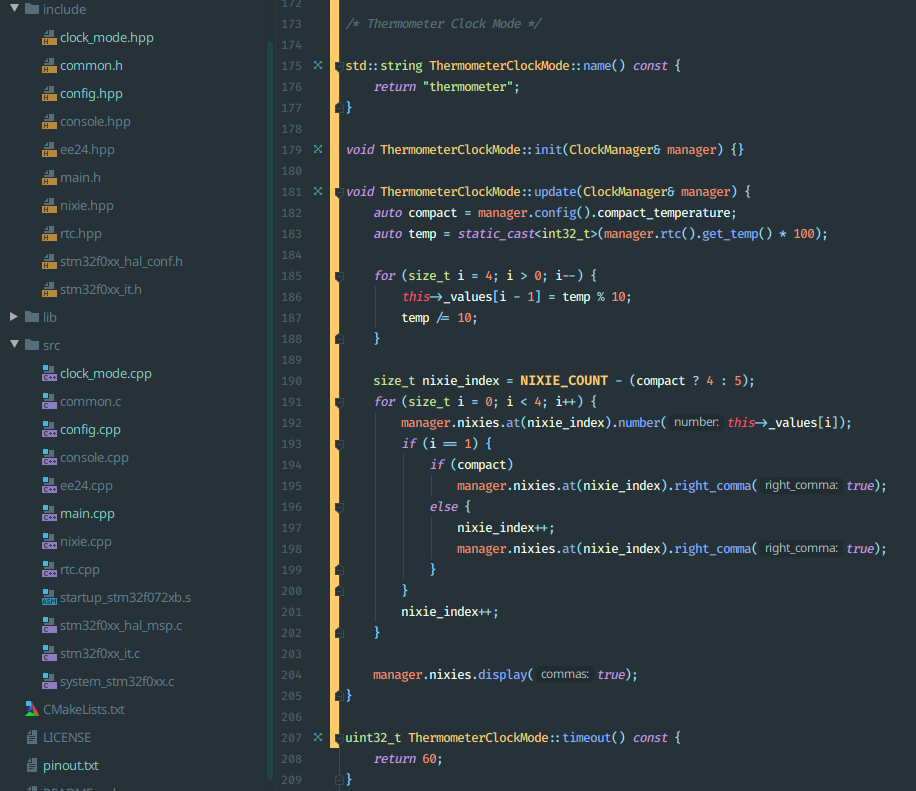
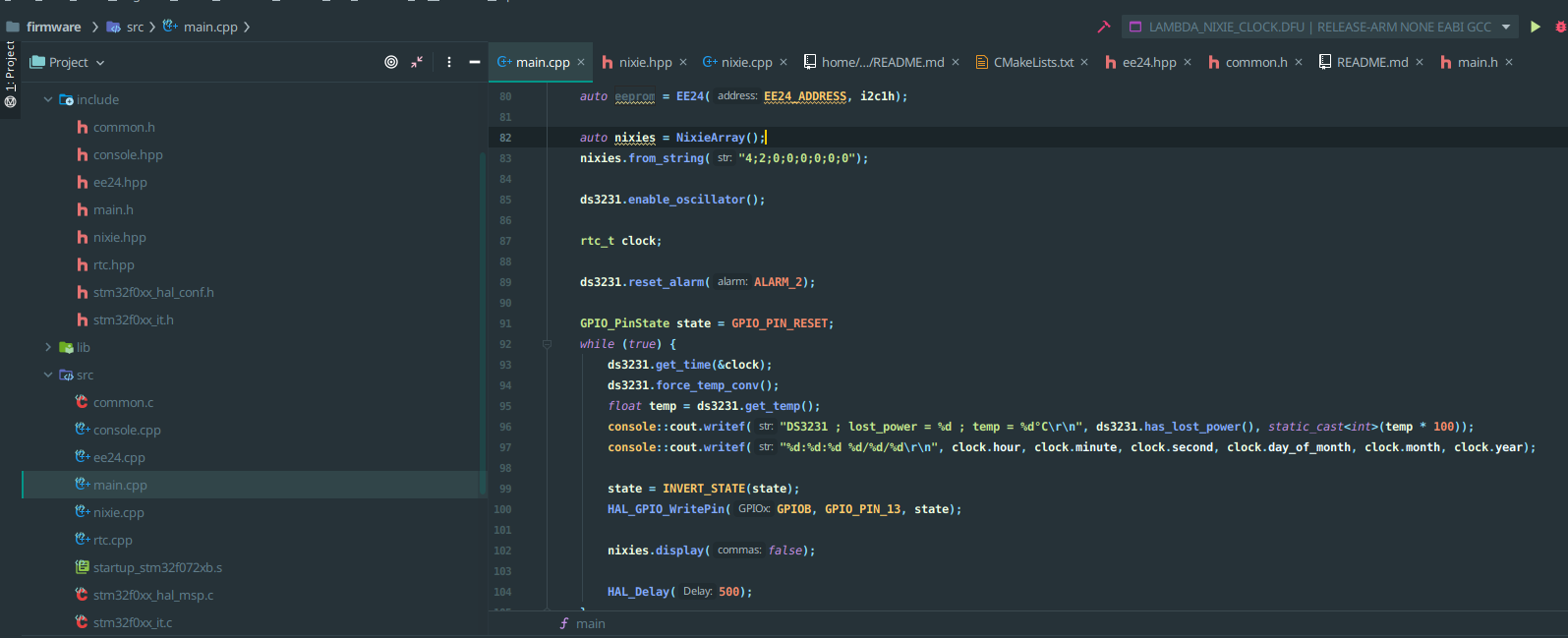
The code below is the code of the thermometer mode, there's two display modes (if there's more than 4 nixie tubes) which just defines if the comma is on the same nixie tube as the last integer digit of the temperature.
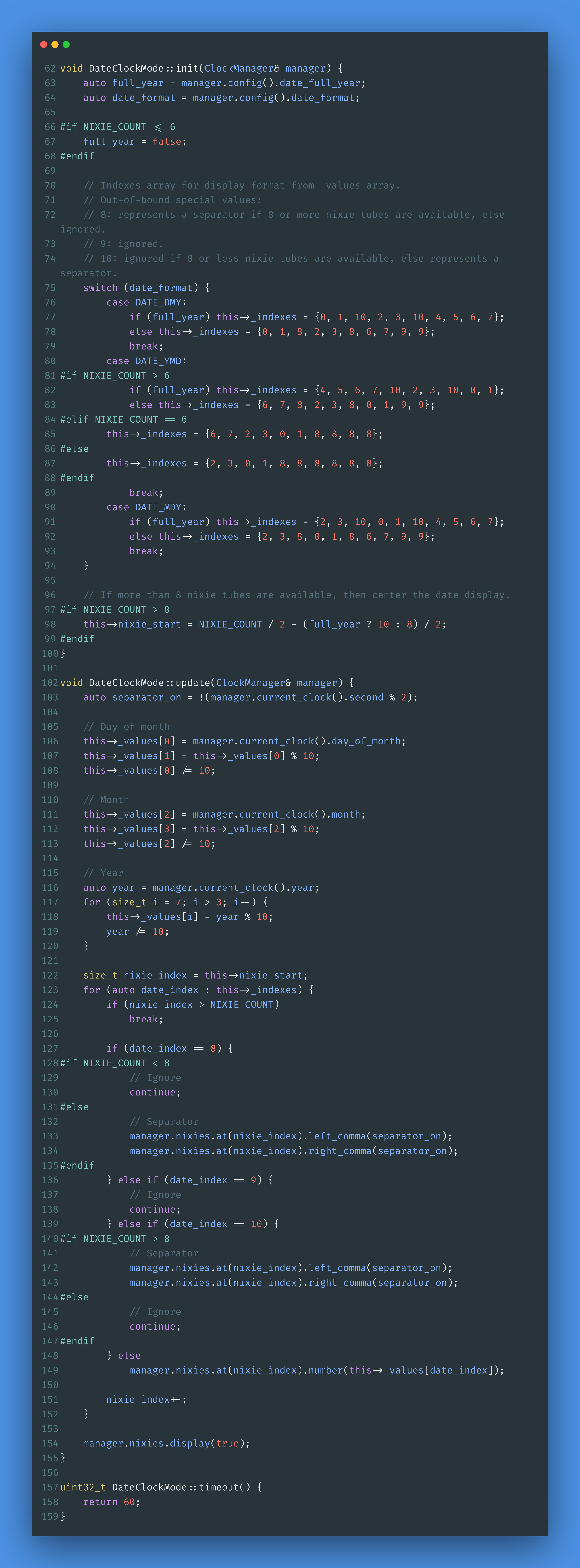
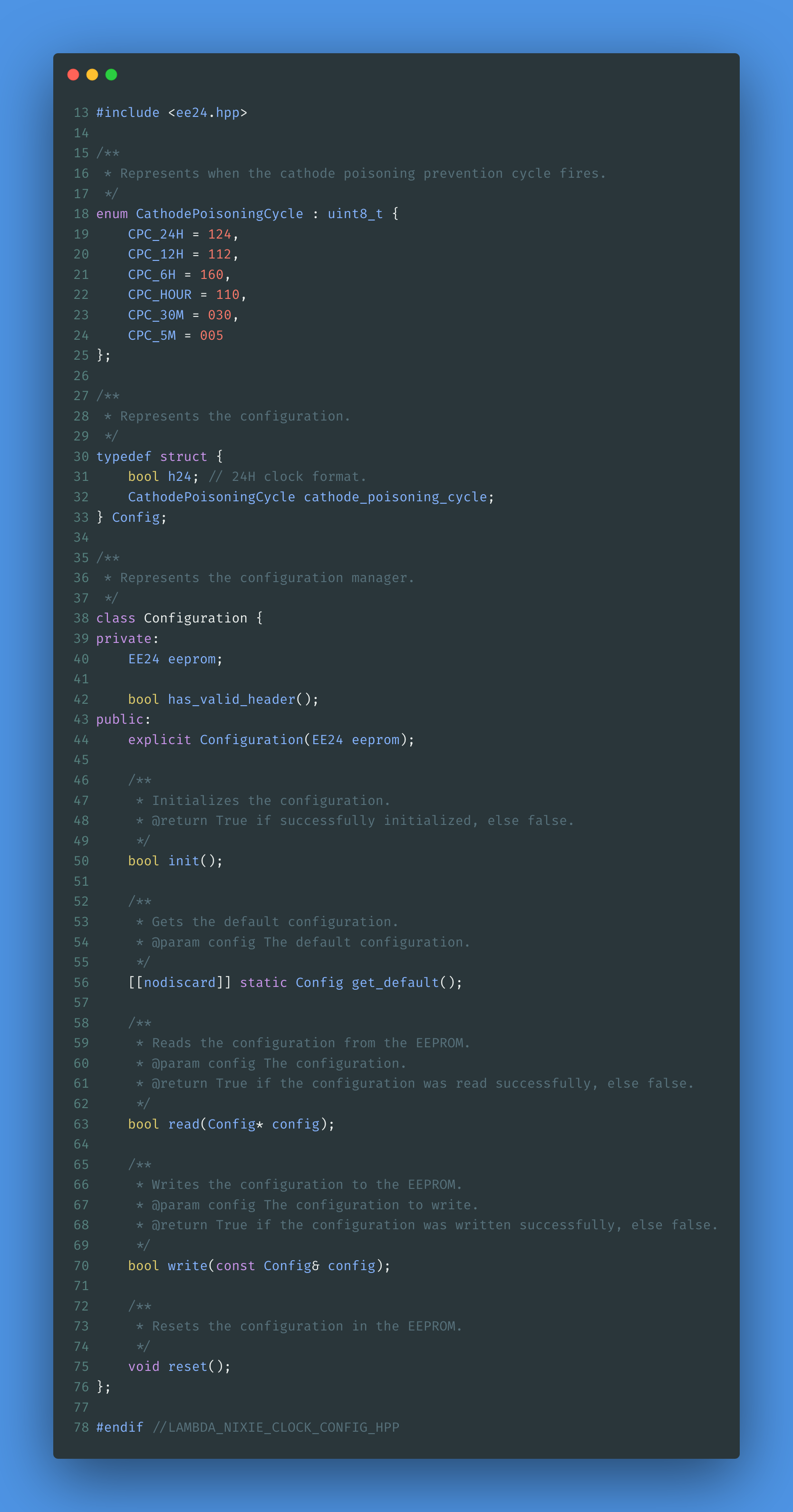
Here's the commit if someone is interested: github.com/LambdAurora/nixie_clock/commit/1ca878372e1efada336288ecba3bab174d6ae272date_full_year which determines if the year is fully displayed or only the two last digits and date_format which is the date format like YMD, MDY and DMY as default. The difficulty was figuring out how to display that correctly in the correct order with 4, 6, 8 or more nixie tubes!
I had the idea to put the date in a 8-bit unsigned int array in the format dd MM YYYY then I have another array which contains the indexes of the first array in an order which depends of the date format! It allowed me to make the display algorithm simple and understandable!
If anyone interested, here's the commit: github.com/LambdAurora/nixie_clock/commit/c37c5d1f649f646f165d2cd6f450de5699b74d43update method and timeout to fall back to the default mode if no interaction was done for a certain amount of seconds.
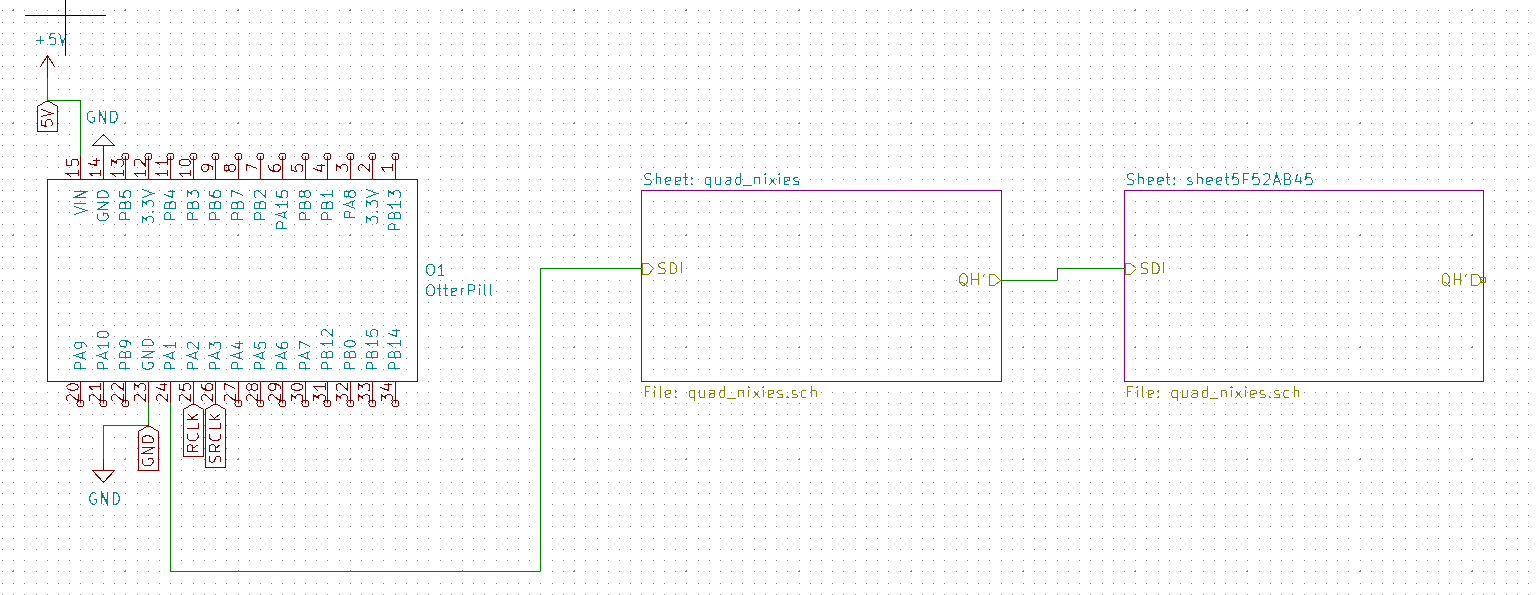
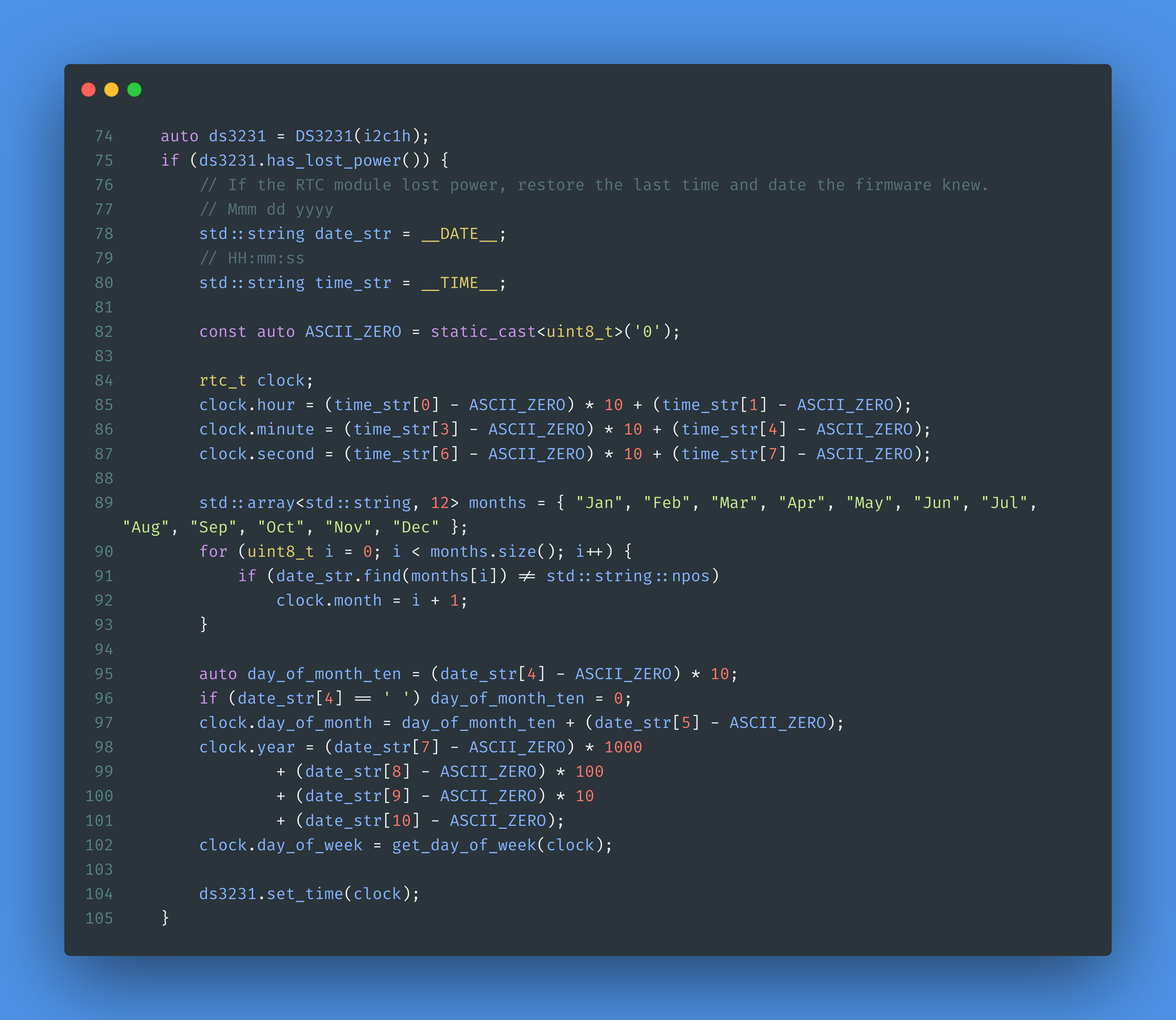
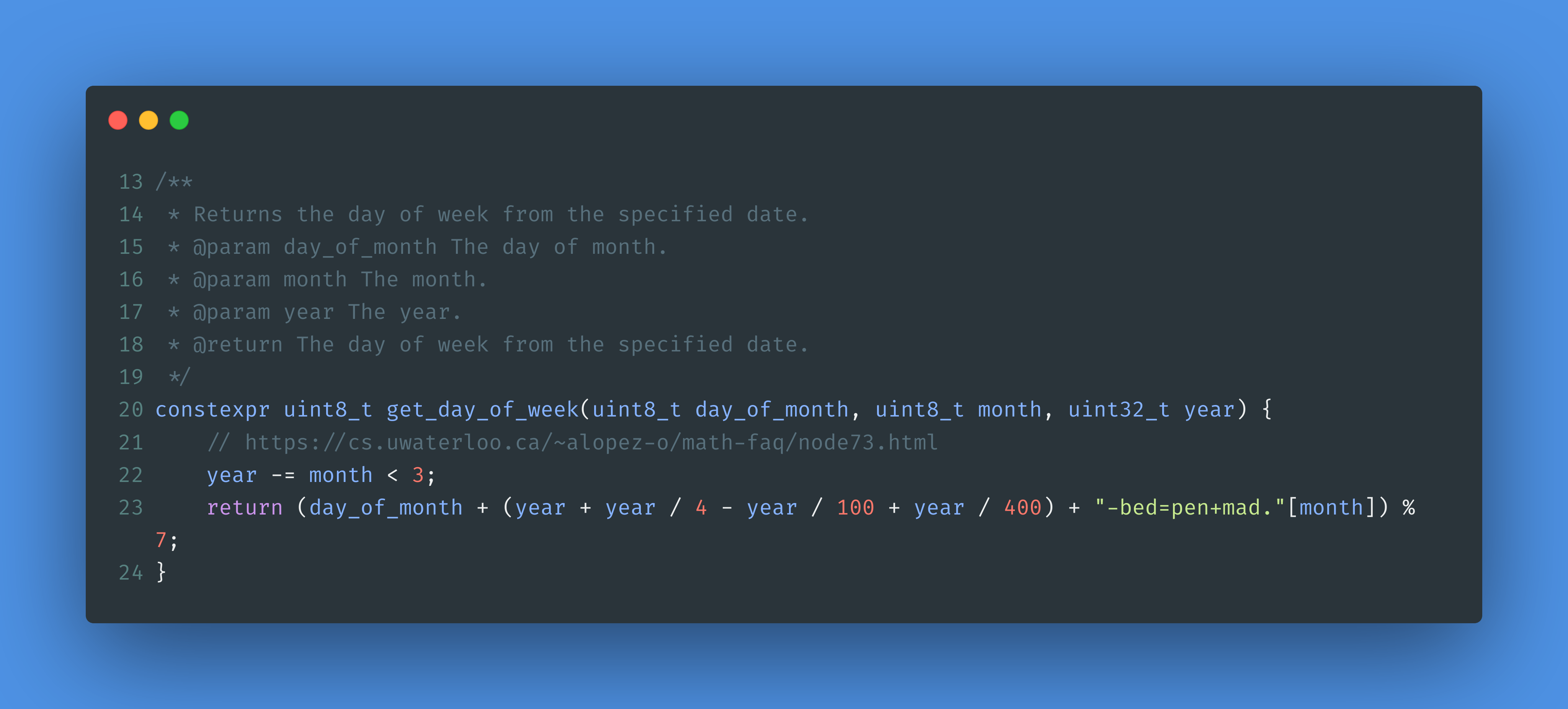
I also added a code for the RTC module in case it losts power (but it shouldn't with its battery), in the case it lost power it will restore the last time and date the firmware knew which is its compilation time & date! I also had to search for an algorithm to determine the day of week from year, month and day of month; and I found the answer on the website of a Canadian university with a C code from 1993.
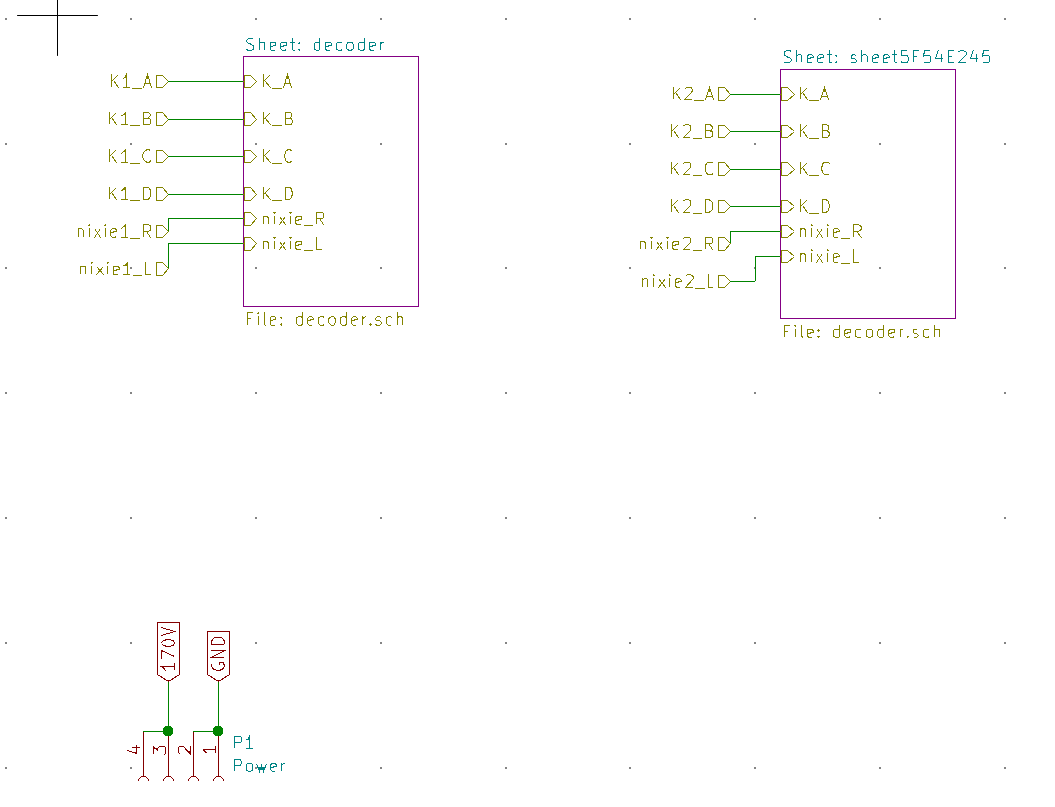
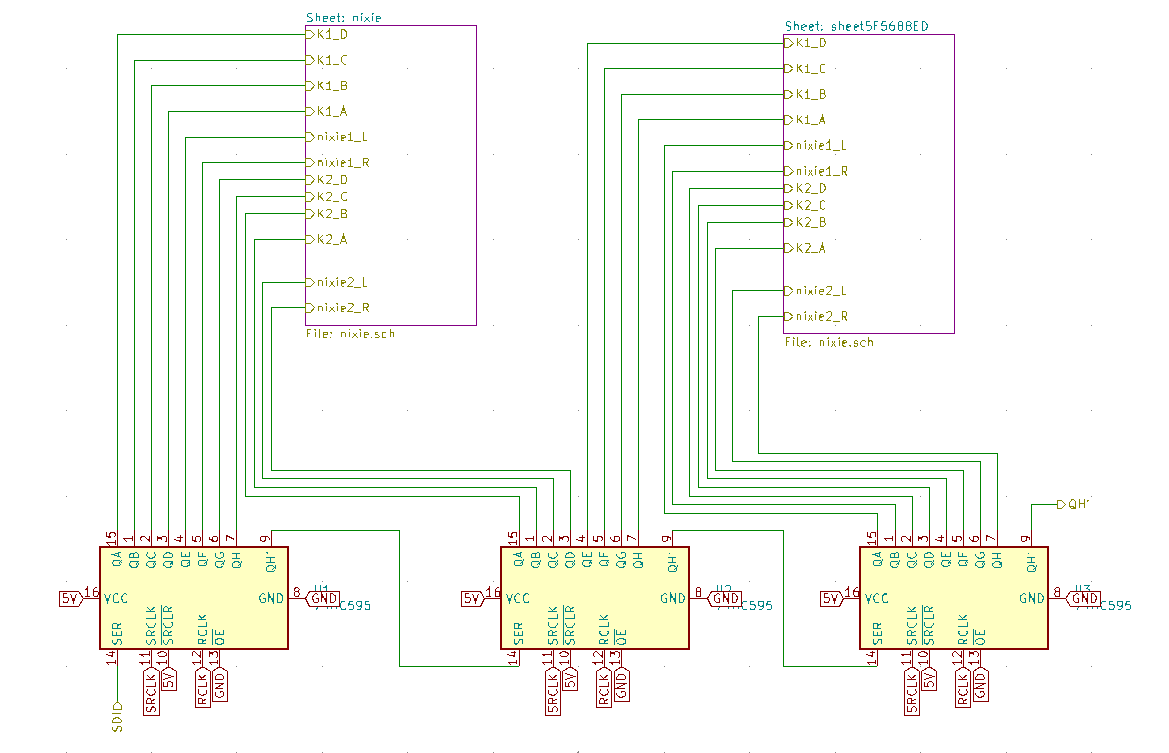
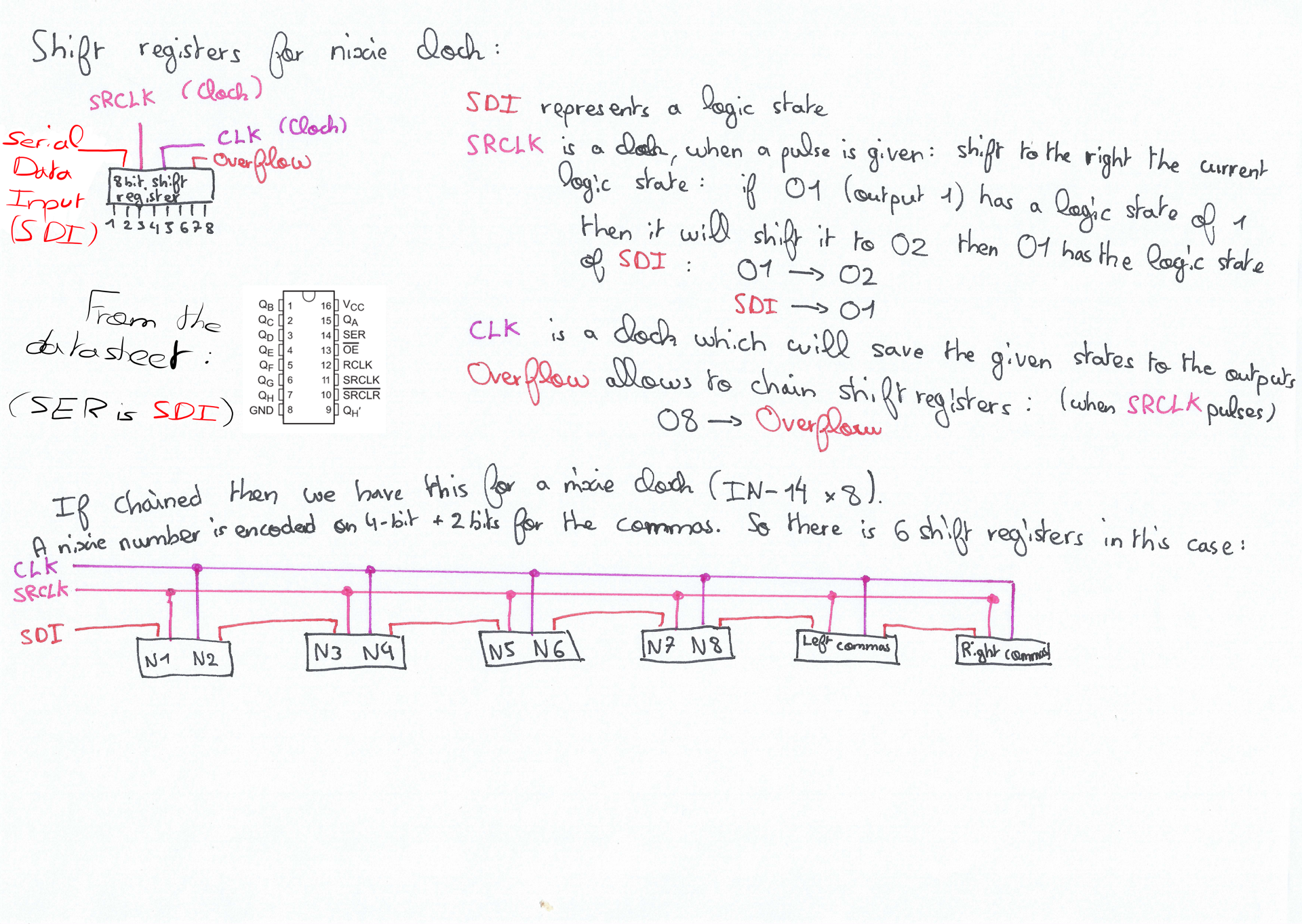
If anyone wants to see the changes: github.com/LambdAurora/nixie_clock/commit/22cac8b004324ba2eb293c8547379e5909bbe7e3nixies variable which is the result of the work on that algorithm. (and nixie.hpp/nixie.cpp)
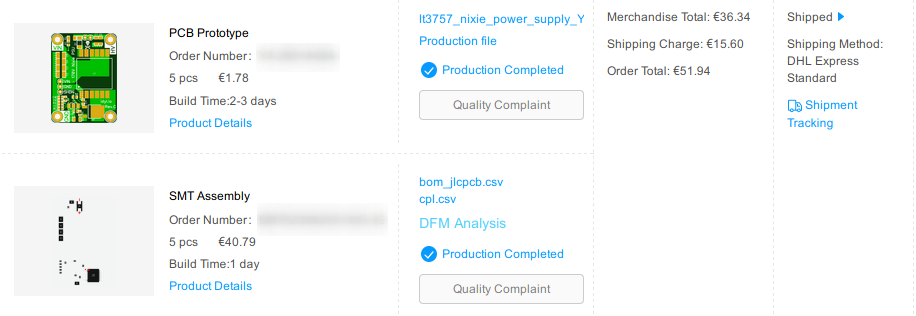
And I pushed it to GitHub (github.com/LambdAurora/nixie_clock/commit/04bec99740df109aa000040f4ac211a3f8c4e43f)!